Kidney Cancer
Overview
What is the Kidney Cancer?
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, is a disease wherein the kidney cells start growing uncontrollably and become cancerous or malignant. he incidence of kidney cancers is relatively higher in developed countries.
Epidemiology
It is less common in eastern countries, according to the reports. Kidney cancer is one of the cancers that can be easily treated. They also have excellent survival rates, and patients can lead a normal and healthy life after the treatment.
Causes
Although the exact cause of kidney cancer is not known, a few risk factors have been identified, and these risk factors are found to increase one’s chances of developing kidney cancer:
Smoking: Smoking doubles kidney cancer risk.
Obesity: Obese individuals are prone to developing kidney cancers.
Family History of Kidney Cancer: Having a positive family history of kidney cancer is a risk factor for kidney cancer.
Regular Usage of NSAIDs: Consumption of ibuprofen and naproxen for a long time is associated with an increased risk of kidney cancer.
Underlying Kidney Diseases: Being diagnosed with kidney disorders that need dialysis increases one’s risk of developing kidney cancer.
Infection: Hepatitis C infection increases kidney cancer risk.
Age: The risk of kidney cancer increases with age.
Diagnosis
There are multiple tests recommended by doctors for the detection and diagnosis of kidney cancers. Before any test, a thorough physical examination and medical history assessment are done in order to understand the cause of the signs of symptoms that a patient has presented oneself with:
a. Blood Tests: Blood tests do not help with a definitive diagnosis, but they can hint at an underlying kidney problem that needs medical attention.
b. Urine Cytology/Urine Tests: Urine tests are also recommended to check for traces of blood, which are only visible under a microscope.
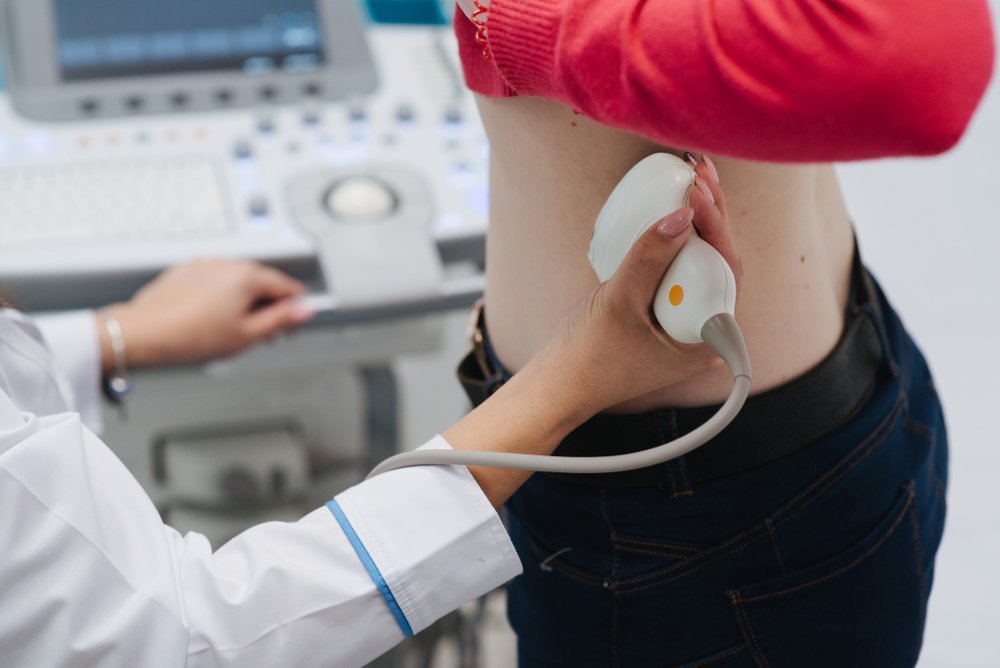
c. Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as MRI scan, PET/CT scan, etc.
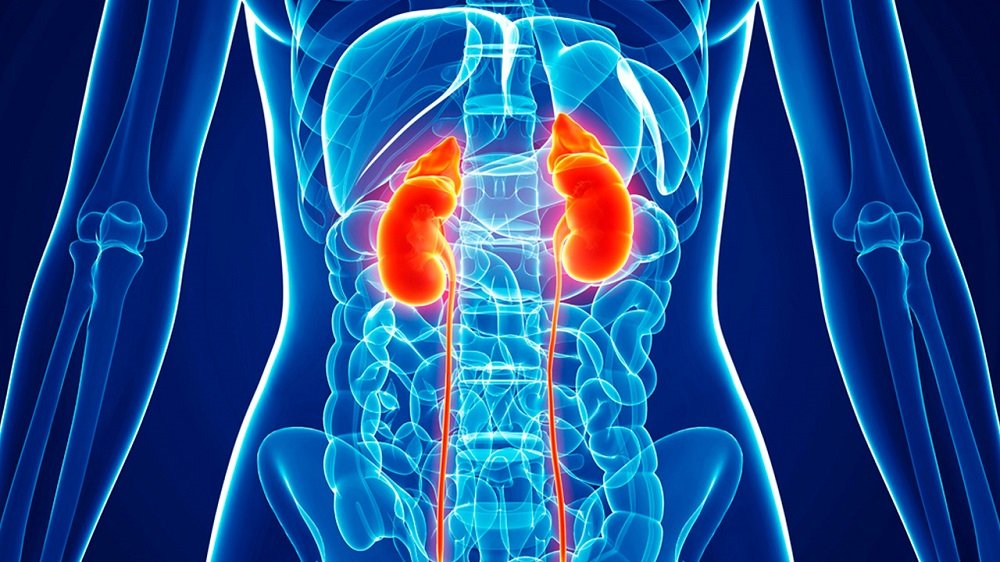
Treatment
The treatment suggested by the doctor depends on the stage of kidney cancer. It may also depend on other factors, such as the size of the tumor, exact location, underlying medical conditions, the patient’s age and overall condition of the patient. Following are the treatment options available for kidney cancer:
For patients who are too old to undergo aggressive treatment or have a smaller tumour or are diagnosed with other serious medical conditions like heart disease, lung disease or kidney disease, active surveillance may be recommended. During active surveillance, the doctor will closely monitor the tumour through regular tests and appointments.
Surgery: Surgery is the main line of treatment for kidney cancers. Kidney tumors can either be operated through open surgery or minimally invasive surgery. Minimally invasive procedures include robotic surgery and laparoscopic surgery; both these procedures use tiny incisions to insert the instruments and operate the tumour. Reduced blood loss, fewer treatment-related complications, lesser pain and faster recovery are some of the advantages of minimally-invasive procedures.
It is a non-invasive medical procedure that uses high-energy radiation beams, such as X-rays to destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy may be combined with other treatment modalities, such as surgery and chemotherapy in order to enhance the overall effectiveness of the treatment.