Acute Myeloblastic Leukemia
Overview
What is the Leukemia?
As the disease progresses, leukaemic blast cells get into the bloodstream and accumulate in various organs, namely lymph nodes, spleen, liver and central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). ALL is more prevalent among children than it is among adults.
What is Acute Myeloblastic Leukemia?
Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is a type of blood cancer that starts in the bone marrow. Through the bloodstream, it may spread to other body parts, such as lymph nodes, liver, spleen, central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), and testicles in advanced stages.
Causes
Although the exact causes of AML are unknown, there are a few risk factors that are associated with this disease:
Smoking
With age, the risk of AML increases
History of chemotherapy or radiation therapy
History of childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL)
Having myelodysplastic syndrome or a bone marrow failure disease
Congenital disorders like Down’s Syndrome
Gender (AML is more common among men)
Exposure to hazardous radiation,
Exposure to benzene.
Diagnosis
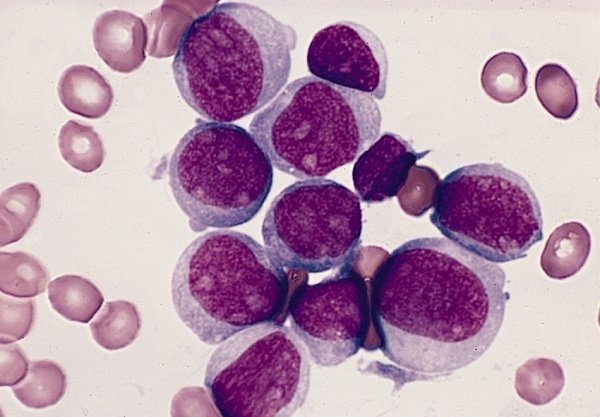
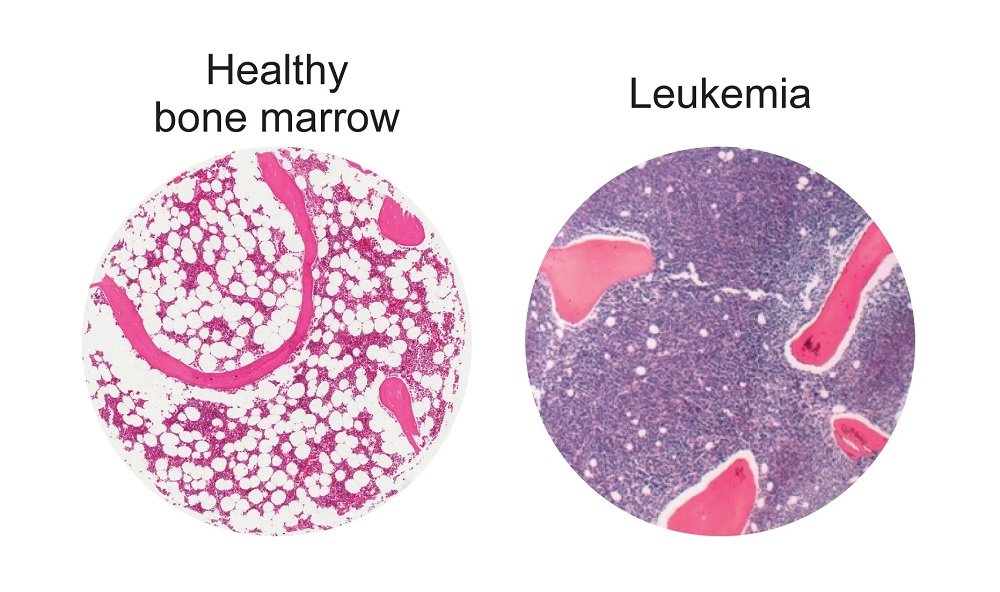
AML can be diagnosed with a simple blood test wherein the sample drawn is examined under the microscope for any abnormalities. If abnormal cells are found, a bone marrow aspiration or trephine biopsy may follow. This helps in classifying the type of acute leukaemia accurately.
A flow cytometry assessment and cytogenetics assessment using peripheral or bone marrow aspirate helps in identifying the AML’s immunophenotype and determining the prognosis.
A lumbar puncture may be recommended if brain metastasis is suspected.
Treatment
AML is one such cancer that progresses quickly, and therefore, it has to be treated as soon as it is diagnosed. Multiple factors are to be considered before devising a treatment plan, and they include the subtype and stage of AML, the patient’s age and the overall health. Following are the common methods used to treat AML:
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the main line of treatment for acute myeloid leukaemia in most cases. Chemotherapy is administered in three different phases, namely:
- Induction
- Consolidation
- Maintenance
Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant
Haematopoietic stem cell transplant or stem cell transplant is a curative treatment approach wherein the stem cells extracted from HLA-matched donors are transferred to the patient’s body after the leukaemic cells are destroyed by chemotherapy.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is a non-standardised treatment for AML, and it is recommended when the disease has spread to the brain or spinal cord.
During radiation therapy, the cancer cells are precisely targeted with high-dose radiation beams. The radiation destroys the cancer cells while minimising damage to the surrounding healthy tissues.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is a personalised treatment approach where the specific genes, the components released or the tissue environment that supports the growth of leukaemic cells are targeted. This treatment blocks the growth of leukaemic cells and also prevents them from spreading to other organs. Targeted therapy also minimises damage to the healthy tissues.

